Unit: 5 Work Study
Unit: 5 Work Study (Theory)
Syllabus
- 5.1 Work Study Method Study- Objectives, Selection of work;
- 5.2 Basic procedure for conduct of Method study, Flow process chart (Names only), Flow Process chart symbols,
- 5.3 Work Measurement – Objectives, steps involved in work measurement
- 5.4 Time study, procedure of Time Study, Time Study Equipment.
- 5.5 Standard Time, Allowances, PMTS.
5.1 Work Study Method Study- Objectives, Selection of work
Work Study
Work study is a systematic approach to examine and analyze the way work is performed in an organization with the aim of improving efficiency, productivity, and overall work methods. Work study is a valuable management tool that aims to optimize work processes, enhance productivity, improve working conditions, and ultimately contribute to the overall success and efficiency of an organization.
Work study is the investigation, by means of a continuous system of the work done in an organization, in order to attain the best utilization of resources i.e. Materials, Machines, Men and Money. All the management systems are related to the productivity of an organisation. Work study is one of the basic techniques of improving productivity.
Generally, work study is used to describe a complete set of techniques with the help of which work can be simplified, standardized and measured.
Objectives of work study
Method Study:
One of the main objectives of work study is to analyze and improve the methods used in performing various tasks. This involves examining the sequence of operations, movements, and processes involved in a particular job or task, and finding ways to simplify or streamline them. The goal is to eliminate unnecessary movements, reduce fatigue, and increase efficiency.
Work Measurement:
Work study also involves measuring the time required to perform a specific task or operation using techniques such as time study, work sampling, or predetermined motion time systems. This helps in establishing standard times for different tasks, which can be used for planning, scheduling, and setting performance standards.
Workplace Design:
Work study plays a crucial role in designing or modifying workplaces, workstations, and work environments. It helps in determining the most ergonomic and efficient layout, equipment, and tools required for a particular job, taking into account factors such as safety, comfort, and productivity.
Productivity Improvement:
One of the primary objectives of work study is to increase productivity by identifying and eliminating bottlenecks, reducing waste, and optimizing the use of resources (e.g., labor, materials, equipment). This leads to cost savings and improved overall efficiency.
Standardization:
Work study helps in establishing standard practices, procedures, and methods for performing various tasks. This promotes consistency, reduces variability, and facilitates training and knowledge transfer.
Employee Motivation:
By involving employees in the work study process and incorporating their suggestions, it can contribute to increased job satisfaction, motivation, and a sense of ownership over their work.
Techniques of Work Study
Basically, there are two techniques of Work Study
- Method Study
- Work Measurements
Method Study
Method study is the process that specifies the methods and activities considered in a job through and eliminates unnecessary elements of operations to obtain the fastest and the best method of performing a specific job. It is the systematic recording and critical examination of existing and proposed ways of doing a work as a means of developing and applying easier and more effective methods as well as reducing costs.
Method Study Techniques:
- Motion Study
- Micromotion Study
- Process Analysis
- Flow Process Charts
- Operation Process Charts
- Ergonomic Studies
- Value Analysis
These techniques are primarily focused on analyzing and improving the methods or procedures involved in performing a task or operation. They aim to simplify, streamline, and optimize the way work is carried out, eliminate unnecessary movements, and improve efficiency.
1. Motion Study:
This technique involves analyzing the movements involved in performing a task or operation. It aims to eliminate unnecessary movements, reduce fatigue, and improve the efficiency of the work method. Analyzing the movements involved in a worker loading boxes onto a conveyor belt, with the aim of reducing unnecessary motions and improving efficiency.
2. Micromotion Study:
This is a more detailed form of motion study, where the individual movements and motions involved in a task are recorded and analyzed using devices like a film camera or a video recorder. Recording and analyzing the detailed hand and finger movements of a worker performing a intricate task, such as assembling a small electronic device, using a video camera.
3. Process Analysis:
This involves systematically examining and documenting the sequence of activities and operations involved in a process. It helps identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for process simplification or improvement. Documenting and examining the sequence of steps involved in the process of serving a customer at a fast-food restaurant, from taking the order to delivering the food.
4. Flow Process Charts:
These are graphical representations of the sequence of operations, movements, and delays involved in a process. They provide a visual representation of the process flow and help identify areas for improvement. Creating a graphical representation of the flow of operations involved in the manufacturing process of a product, such as a car, showing the movement of materials and components.
5. Operation Process Charts:
These charts provide a detailed analysis of the different operations involved in a task or process, including the movements, tools, and materials used.
Ex. Detailing the individual operations, movements, and materials involved in a worker assembling a piece of furniture, including the tools used and the sequence of steps.
6. Ergonomic Studies:
These studies focus on analyzing the physical and cognitive demands of a task or process on the worker. They aim to improve the design of workstations, tools, and equipment to reduce strain, fatigue, and potential injuries.
Ex. Evaluating the physical demands and postures required for a worker operating a computer workstation, with the aim of designing an ergonomic setup to reduce strain and potential injuries.
7. Value Analysis:
This technique involves analyzing the components or activities of a product or process to determine their relative importance and potential for cost reduction or elimination.
Ex. Examining the components and features of a product, such as a smartphone, to determine their relative importance and potential for cost reduction or elimination, while maintaining essential functions.
Work Measurements
Work measurement is the application of techniques designed to establish the time for qualified worker to carry out a job at a defined level of performance.
For example, publishing a book is a production process. There are many elements, which are involved in the publication of a book. Book publication involves production steps like typing a manuscript, editing the written matter, proof reading it, followed by printing and binding.
Work measurement involves finding out the time taken for doing each element. The time taken for each element is added with each other. This is the standard time for publishing the book. Here, provisions are also made for relaxation, breakdown of machines, etc.
Work Measurement Techniques:
- Time Study
- Work Sampling
- Man-Machine Charts
These techniques are primarily concerned with measuring the time required to perform a specific task or operation. They help establish standard times, identify bottlenecks, and provide data for planning, scheduling, and setting performance standards.
1. Time Study:
This technique involves measuring the time taken by a qualified worker to perform a specific job or operation under normal working conditions. It helps establish standard times for different tasks and identify opportunities for improvement. Measuring the time taken by a worker to assemble a bicycle, under normal working conditions, to establish a standard time for the task.
2. Work Sampling:
This technique involves randomly observing workers at different intervals to record their activities. It helps determine the proportion of time spent on various activities and identify areas for improvement. Randomly observing and recording the activities of call center agents at different intervals to determine the proportion of time spent on answering calls, completing paperwork, and other tasks.
3. Man-Machine Charts:
These charts are used to analyze the relationship between the worker and the machine or equipment used in a process. They help identify idle time, bottlenecks, and opportunities for better coordination. Analyzing the interaction between a worker and a packaging machine, identifying idle times and opportunities for better coordination and utilization of resources.
Difference between method study and work measurement
Method Study | Work Measurement | |
Purpose | Method Study focuses on analyzing and improving the method or way of performing a job or operation, with the aim of simplifying and streamlining the process. | Work Measurement, on the other hand, is concerned with determining the time required to perform a specific job or operation using established methods. |
Emphasis | Method Study emphasizes the qualitative aspects of work, such as the sequence of operations, movements, and flow of the process. | Work Measurement emphasizes the quantitative aspects of work, primarily the time taken to complete a task or operation. |
Techniques | Method Study techniques include process analysis, operation process charts, flow process charts, motion study, and ergonomic studies. | Work Measurement techniques include time study, work sampling, and predetermined motion time systems. |
Objective | The primary objective of Method Study is to develop and apply the most effective and efficient method of performing a job or operation. | The primary objective of Work Measurement is to establish standard times for various operations, which can be used for planning, scheduling, and setting performance standards. |
Implementation | Method Study is typically carried out first to improve and streamline the work method before applying Work Measurement techniques. | Work Measurement techniques are applied to the improved method developed through Method Study to determine the standard time for the operation. |
5.2 Basic procedure for conduct of Method study, Flow process chart, Flow Process chart symbols
Procedure of Method Study
- Step 1 Select: The first step of method study is to select a job, activity or process to improve.
- Step 2 Obtain and Record: Obtain the facts about the existing methods related to the job and record it.
- Step 3 Examine: Examine the facts critically. It is concerned with questioning the different activities of the process in a systematic, logical and objective manner.
- Step 4 Develop: The next step of method study is to develop the improved method.
- Step 5 Install: Install the improved method. This involves training of those who are going to perform the new method.
- Step 6 Maintain: The last step in method study is to maintain the improved method.
Flow Process Chart:
Flow Process Charts are graphical tools used in method study to provide a visual representation of the sequence of events, operations, movements, and delays involved in a process or procedure. They help analyze and understand the flow of materials, information, or people through a series of steps, making it easier to identify areas for improvement, bottlenecks, or inefficiencies.
Flow Process Charts use a set of standard symbols to represent different activities or events in the process. Here are the commonly used symbols in Flow Process Charts:
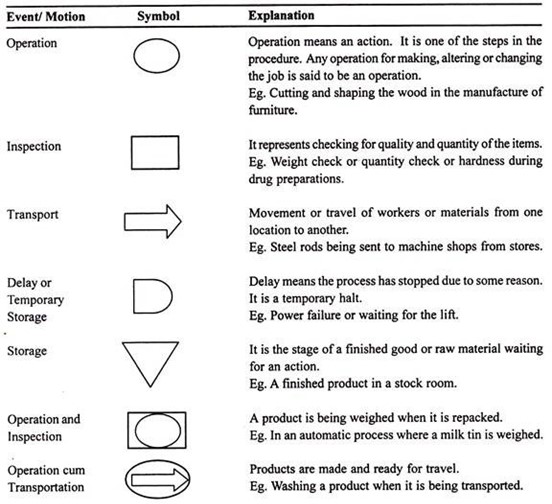
5.3 Work Measurement – Objectives, steps involved in work measurement
Work Measurements (as we have discussed in section 5.1)
Work measurement is the application of techniques designed to establish the time for qualified worker to carry out a job at a defined level of performance.
For example, publishing a book is a production process. There are many elements, which are involved in the publication of a book. Book publication involves production steps like typing a manuscript, editing the written matter, proof reading it, followed by printing and binding.
Work measurement involves finding out the time taken for doing each element. The time taken for each element is added with each other. This is the standard time for publishing the book. Here, provisions are also made for relaxation, breakdown of machines, etc.
Objectives of Work Measurement
- (1) Target time for each job can be scientifically estimated, with this estimate realistic schedules and manpower requirements can be prepared.
- (2) Comparison of alternative methods is possible.
- (3) Useful wage incentive schemes can be formulated on the basis of target times.
- (4) In can lead to proper balancing of the work distribution.
- (5) To standardize the efficient method of performing operations.
- (6) To standardize conditions for efficient performance.
- (7) To determine man and machines ratio for effective and efficient utilization of both.
- (8) To provide information’s and basis for production planning and scheduling activities.
Steps in Work Measurement
Select | The work to be studied. |
Record | All the relevant data relating to the circumstances in which the work is being done, the methods and the elements of activity in them. |
Measure | Each element in terms of time over a sufficient number of cycles of activity to ensure that a representative picture has been obtained. |
Examine | The recorded data and element times critically to ensure that unproductive or random elements are separated from productive elements; the recorded times of each element and determine a representative time for each. |
Compile | Time for the operation, which will provide a realistic standard of performance and will include time allowances to cover suitable rest, personal needs, contingencies, etc. |
Define | Precisely the series of activities and method of operation for which the time has been allowed and issue the time as standard for the activities and methods specified. |
Work Measurement Techniques we have discussed before in section 5.1
5.4 Time study, Procedure of Time Study, Time Study Equipment
Time study
This technique involves measuring the time taken by a qualified worker to perform a specific job or operation under normal working conditions. It helps establish standard times for different tasks and identify opportunities for improvement.
Ex. Measuring the time taken by a worker to assemble a bicycle, under normal working conditions, to establish a standard time for the task.
According to International Labour Organisation (1974), “Time Study is a work measurement technique for recording the times and rates of working for the elements of a specified job carried out under specified conditions, and for analyzing the data so as to obtain the time necessary for carrying out the job at a defined level of performance”.
Basic Steps in The Time Study
- To permit the rate of working to be assessed more accurately than would be possible if the assessments were made over a complete cycle.
- Enable the different types of elements to be identified and distinguished, so that each may be accorded the treatment appropriate to its type.
- Enable elements involving high fatigue to be isolated and to make the allocation of fatigue allowances (extra benefits for high fatigue work) accurately.
- Checking the method so that the subsequent omission or insertion of elements may be detected quickly. This may become necessary if at a future date the time standard for the job is queried.
- Enable a detailed work specification to be produced.
- Enable time values for frequently recurring elements, such as the operation of machine controls or loading and unloading work pieces from fixtures, to be extracted and used in the compilation of data.
Time Study Equipment
- (i) Stop-watch
- (ii) A Study board
- (iii) Pencils (writing /marking)
- (iv) Time Study forms
- (v) Slide rule (for speeding up calculations), and
- (vi) Measuring instruments for distance and speed such as rulers, tapes micrometre, technometer etc.
5.5 Standard Time, Allowances, PMTS
Standard Time (in work study)
In work study, the standard time is defined as the time required by an average skilled operator working at a normal pace to perform a given task or operation, following the prescribed method and under standard working conditions.
The standard time includes the following components:
Normal time:
This is the time taken by an average skilled operator working at a normal pace to complete a task or operation. It is determined through time study observations and rated based on the operator’s performance.
Allowances:
These are additional time allowances added to the normal time to account for:
- a) Personal allowances: Time for personal needs like drinking water, going to the restroom, etc.
- b) Fatigue allowances: Time to compensate for physical and mental fatigue.
- c) Contingency allowances: Time for unavoidable delays, interruptions, or interferences in the work process.
The standard time is calculated as: Standard time = Normal time + Allowances
The standard time serves as a benchmark for planning, scheduling, and evaluating the performance of workers. It helps in setting realistic production targets, determining labor costs, and identifying opportunities for process improvement. Standard times are established through careful time study observations and analysis, considering the prescribed method, working conditions, and allowances for personal, fatigue, and contingency factors.
Pre-Determined Motion Time Systems (PMTS)
It is a work measurement technique, which involves breaking down work tasks into fundamental motions or elements and assigning predetermined times to each of these motions Basic human motions are tabulated with time standard for each basic human motion. The objective is to establish standardized times for performing specific tasks under defined conditions.
Pre-Determined Motion Time Systems play a crucial role in work study in management by providing a systematic approach to measuring, analyzing, and improving work processes, ultimately leading to greater efficiency, productivity, and cost-effectiveness.
——End of Unit 5 Notes——
Previous Year Questions:
2023 July Work Organisation Management Semester 6 Question Paper